Introduction to Dermatitis disease
What is Dermatitis disease?
Dermatitis disease is a general term that describes conditions characterized by skin inflammation. It presents as a red, itchy, and sometimes swollen rash, which can occur on any body part. The term encompasses a range of disorders, including eczema, dandruff, and rashes caused by contact with specific substances. Dermatitis can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life, leading to discomfort and, in severe cases, pain. Although it is a common condition, the symptoms and severity vary widely among patients. Understanding dermatitis is critical to managing its symptoms effectively, as it involves recognizing triggers and implementing preventive measures and appropriate treatments to alleviate the discomfort it causes.
Types of Dermatitis disease
There are several types of dermatitis, each with distinct causes and symptoms. Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is the most common form, often starting in childhood and characterized by dry, itchy skin. Contact dermatitis arises from skin contact with irritants or allergens, leading to localized redness and itching. Seborrheic dermatitis affects oily areas of the body, causing scaly patches and dandruff. Other types include dyshidrotic dermatitis, which affects the hands and feet, and stasis dermatitis, occurring when poor circulation leads to skin problems on the lower legs. Identifying the type of dermatitis is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Understanding the Causes
The causes of dermatitis vary depending on the type. Genetic factors play a significant role in atopic dermatitis, where a family history of the condition or other allergic diseases is common. Contact dermatitis results from exposure to irritants like detergents or allergens such as nickel. Seborrheic dermatitis may be influenced by yeast that lives on the skin, while environmental factors like humidity and temperature can exacerbate many forms of dermatitis. Understanding these causes is essential for prevention and management, allowing individuals to avoid known triggers and seek treatments that address the underlying factors contributing to their condition.
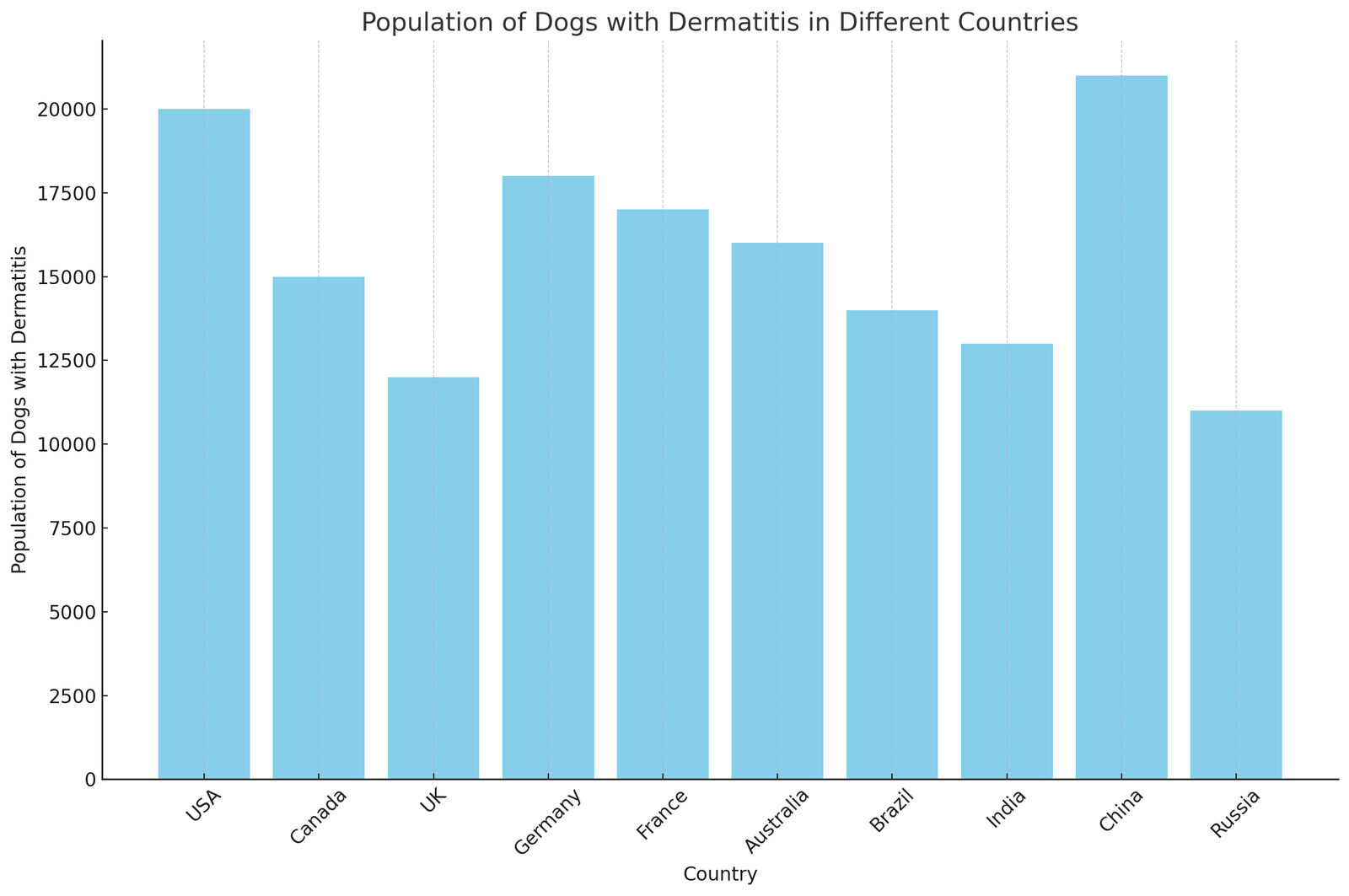
Population Graph of the Dermatitis disease in all over the world
Population Table of the Dermatitis in all over the world
| Year | North America | Europe | Asia | South America | Africa | Oceania |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 3626 | 1372 | 3343 | 2902 | 843 | 2448 |
| 2011 | 4525 | 3979 | 1182 | 2469 | 2980 | 1100 |
| 2012 | 2379 | 3822 | 1608 | 2913 | 1358 | 1829 |
| 2013 | 4699 | 1872 | 1045 | 1046 | 1476 | 1704 |
| 2014 | 2599 | 2999 | 1372 | 2988 | 1280 | 1828 |
| 2015 | 3356 | 2691 | 4065 | 2741 | 1824 | 1086 |
| 2016 | 3819 | 3367 | 3870 | 2798 | 1632 | 660 |
| 2017 | 1159 | 2812 | 4541 | 1441 | 1430 | 1699 |
| 2018 | 4753 | 1416 | 4785 | 1121 | 1084 | 1217 |
| 2019 | 2652 | 1503 | 1451 | 2368 | 2810 | 1403 |
| 2020 | 2243 | 3343 | 1932 | 1264 | 2042 | 1955 |
| 2021 | 3346 | 2695 | 4739 | 1676 | 2311 | 1090 |
| 2022 | 2892 | 4009 | 1892 | 1187 | 894 | 1308 |
| 2023 | 3413 | 4403 | 2425 | 1894 | 2442 | 1761 |
symptoms and Diagnosis
Common Symptoms of Dermatitis
Dermatitis presents a variety of symptoms that can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. These symptoms often include intense itching, redness, and skin inflammation. Some forms of dermatitis, like atopic dermatitis or eczema, can lead to dry, scaly patches that may ooze or crust over, especially when scratched. Contact dermatitis results from exposure to irritants or allergens, causing localized redness, itching, and sometimes blistering. Seborrheic dermatitis typically affects the scalp and face, leading to greasy, flaky skin. These symptoms can fluctuate in severity and may be triggered or worsened by certain environmental factors, stress, or allergens. Recognizing these signs is crucial for timely and effective treatment, as they can closely mimic other skin conditions.
How is Dermatitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing dermatitis involves a comprehensive examination by a healthcare provider, who will assess the skin’s appearance and inquire about symptoms, lifestyle, and possible exposure to allergens or irritants. In some cases, patch testing may be used to identify specific substances causing contact dermatitis. A skin biopsy can help distinguish dermatitis from other skin diseases when the Diagnosis is unclear. Family history and the pattern of symptoms over time are important diagnostic clues for atopic dermatitis. Accurate Diagnosis is essential for effective treatment, as management strategies vary significantly among different types of dermatitis. Understanding the exact kind and triggers of dermatitis allows individuals to avoid exacerbating factors and adopt appropriate skin care routines.