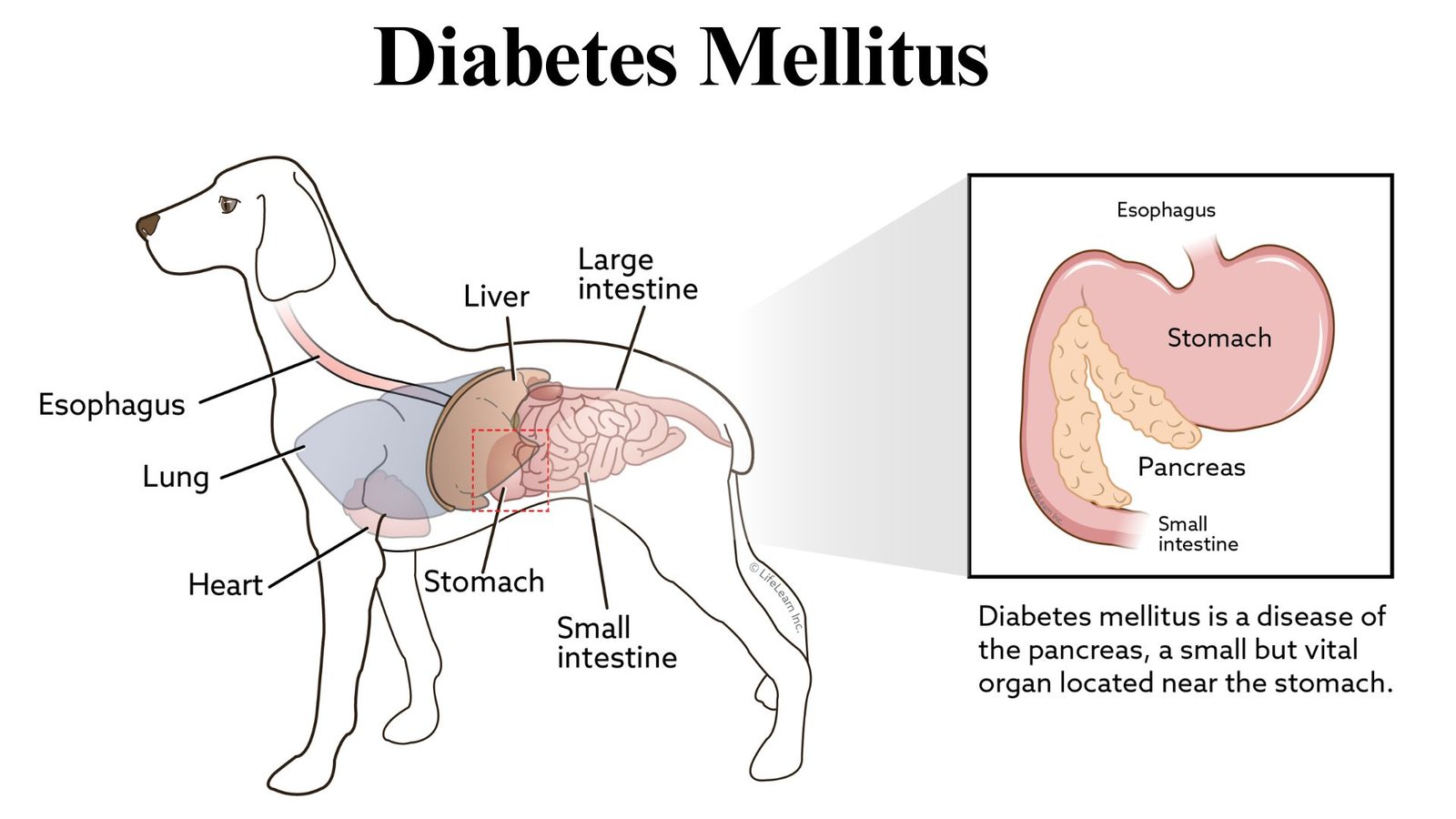
Living with Diabetes
Daily Life and Management
Living with Diabetes requires adopting a mindful approach toward daily routines, encompassing diet, exercise, and medication adherence. Effective management hinges on monitoring blood sugar to make informed nutrition and insulin intake decisions. Individuals learn to recognize the impact of different foods and activities on their glucose levels, leading to a tailored lifestyle that balances diabetes management with personal enjoyment. Education plays a crucial role, as understanding the nuances of the condition empowers people to make healthier choices, navigate challenges, and maintain an active life. Integrating these practices becomes second nature over time, enabling those with Diabetes to lead whole, vibrant lives despite the conditions.
Support Systems
The role of a robust support system in managing Diabetes cannot be overstated. Family, friends, and healthcare professionals form a network of guidance and encouragement, essential for navigating the emotional and physical challenges of the condition. This support extends beyond mere encouragement, offering practical assistance with meal planning, exercise routines, and remembering medication. Online communities and diabetes support groups provide a platform for sharing experiences, tips, and motivation, reinforcing that no one is alone in this journey. Such networks boost emotional well-being and enhance adherence to treatment plans, significantly improving health outcomes.
Coping Strategies and Mental Health
They are maintaining mental health while managing Diabetes is paramount. The constant vigilance required can be overwhelming, leading to stress, anxiety, and even depression. Developing effective coping strategies, such as mindfulness meditation, regular physical activity, and engaging in hobbies, can alleviate stress and promote a positive outlook. Seeking professional help when needed is also vital; therapists and counselors can offer strategies to manage diabetes-related anxiety. Acknowledging and addressing the emotional aspects of living with Diabetes is crucial for holistic well-being, allowing individuals to thrive not just physically but also emotionally and mentally.
Advancements in Diabetes Care
Recent Research and Breakthroughs
In recent years, diabetes care has seen significant advancements thanks to relentless research and technological innovations. One of the most promising breakthroughs is the development of closed-loop insulin delivery systems, often called “artificial”l pancreas” systems.” These devices continuously monitor blood glucose levels and automatically adjust insulin delivery, mimicking the body’s response more closely than ever. Additionally, there have been significant strides in creating ultra-fast-acting insulins and oral insulin formulations, which could revolutionize how insulin is administered, offering more convenience and control over blood sugar levels. Gene therapy and stem cell research also show potential in providing long-term solutions to Diabetes, potentially offering a cure by restoring the body’s production and regulating insulin naturally.
Future Directions in Treatment and Management
The future of diabetes treatment and management looks promising, with several innovative approaches on the horizon. Personalized medicine, driven by genetic advances, is set to tailor treatments to individual patients, optimizing efficacy and minimizing side effects. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems and wearable technology will become more integrated, offering real-time insights into patients’ states and allowing for more precise disease management. Moreover, research into diet, lifestyle factors, and microbiome interventions is expanding, aiming to prevent Diabetes or manage it more effectively without sole reliance on medication. Vaccines for Type 1 diabetes and new classes of medication for Type 2 that not only control blood sugar levels but also address underlying risk factors such as obesity and cardiovascular disease are in development. These advancements signify a shift towards more holistic, patient-centered approaches in diabetes care, emphasizing improving quality of life and reducing long-term complications.
Conclusion
while Diabetes remains a significant health challenge worldwide, understanding its management, embracing healthy lifestyle changes, and staying informed about the latest treatment options can empower individuals to lead fulfilling lives. Although a cure is not yet available, the potential for managing, and in some cases reversing, Diabetes offers hope. By prioritizing prevention, especially for those at higher genetic risk, we can reduce the prevalence of Diabetes and its impact on individuals and healthcare systems alike.